Animals (Game Morality)
在产品游戏化的背景下, 在未来游戏对我们的积极和消极影响都将会放大很多.游戏,这个诞生于人类诞生之初的朋友,对人类社会的影响都需要重新审视一遍。
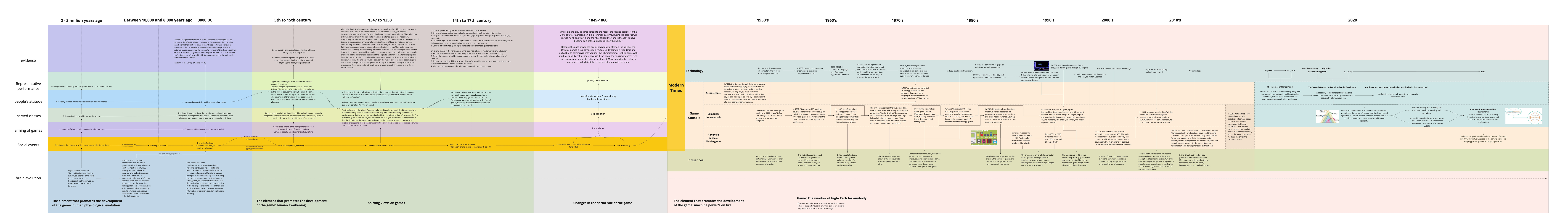
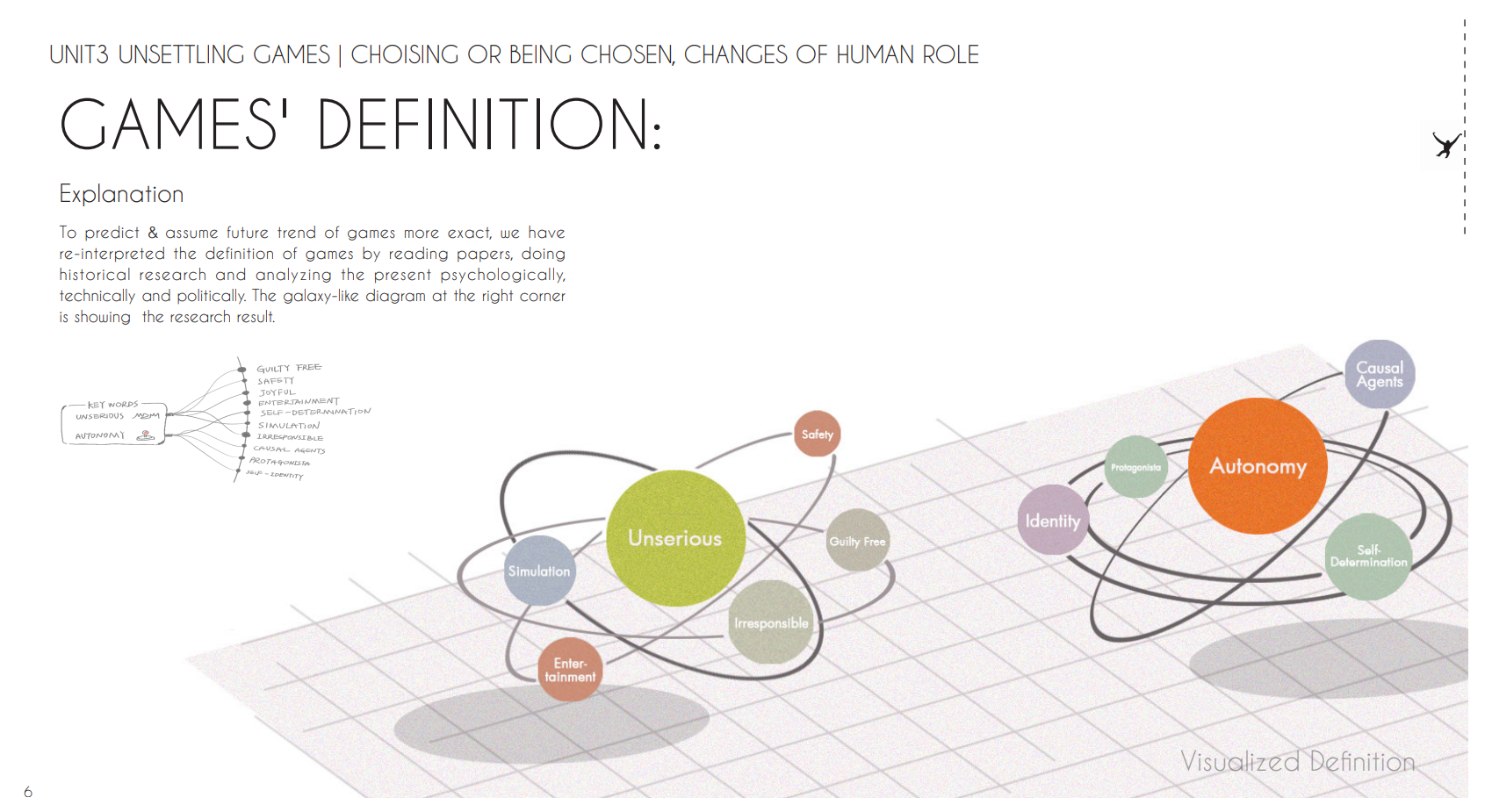
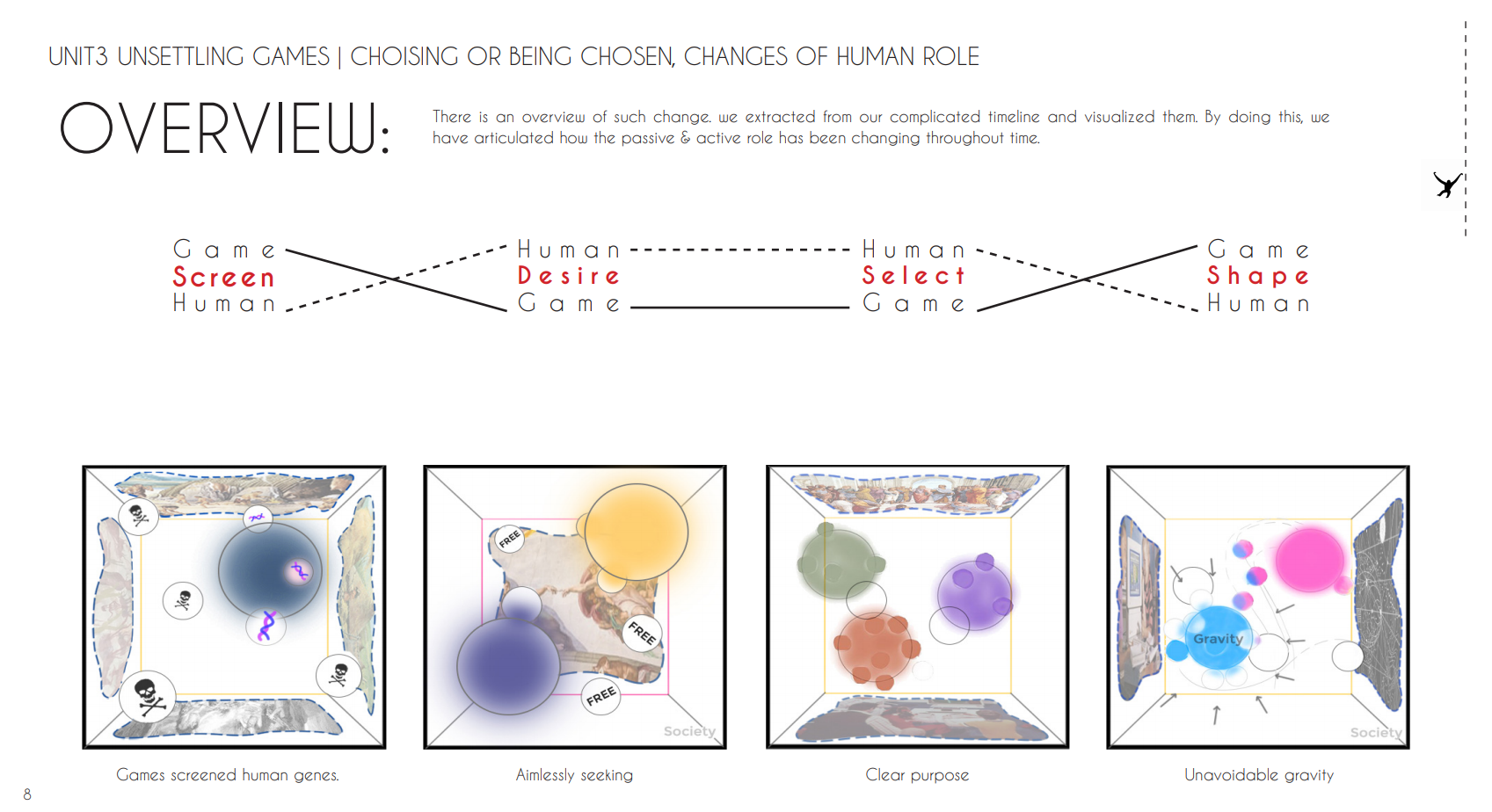
我们发现一个很有趣的问题,过去和现在的很多游戏无法归纳进维基百科游戏的定义(娱乐性,目的性,竞争性),比如过家家、任天堂switch推出的健身换大冒险、动物森友会等等。于是我们重新给出了游戏的定义,即在不严肃环境下完全自主的行为模拟。
我们通过研究几千年前到现在的游戏发展历史发现,人类和游戏关系中的角色一直在发生改变。
在远古时期,偶然诞生的游戏大部分是模拟生存技能训练。懂得通过游戏提高族群战斗力的人类部族基因在优胜劣汰中保存下来。游戏筛选人类。
在文艺复兴时期,人们彻底改变了对游戏的消极态度(中世纪时期,在教廷的影响下,玩和宗教无关的游戏被认为是不洁的行为)。人们在发现自我的同时,解放了对游戏的渴望。随着人性解放的过程,人们各种各样的需求被开发。但受限于当时生产力的低下,人类非常渴望游戏。
如今在各种技术的支持下(如游戏代码开源平台),我们有数不过来的游戏可以选择。人们在挑选时,会更有目的性。比如我喜欢第三人称射击类游戏,我不会在谷歌搜索游戏、射击游戏等模糊概念,而是直接搜索第三人称射击游戏。有的人渴望通过游戏与朋友们社交,有的人希望通过游戏提升自己的某项技能(比如微软公司的飞行模拟游戏)。人类选择游戏的阶段开始了。
我们通过对现象学和行为心理学的研究发现,游戏开始出现shape人类的情况。这种塑造不仅局限于游戏内,在现实生活中也会真实的影响人类个体乃至整个人类社会。我们发现游戏在潜移默化中,通过引诱、使沉迷和使服从这三个手段,改变了我们的行为模式甚至是价值观。
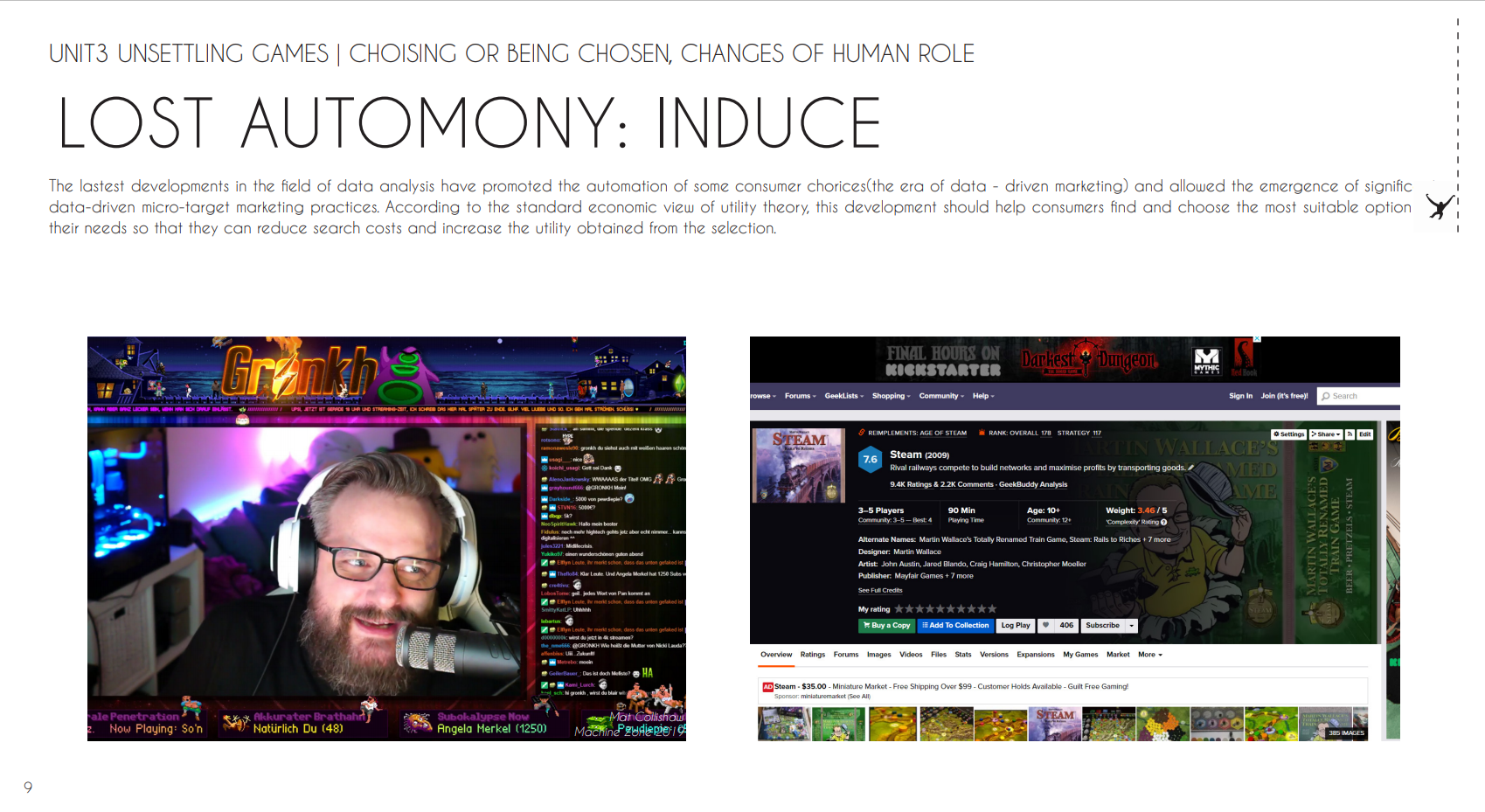
首先,拥有大数据的娱乐公司将会为我们安排他们认为的最适合我们的游戏。那些依靠大数据的算法将比我们自己更清楚我们会需要什么样的游戏。就像人们会花大量的时间在tictok。那些tictok中看似随机刷出的视频其实都是由软件公司的算法提供给我们的。于此同时,由于现在许多游戏公司很多属于一些娱乐企业的一部分。在这样的情况下,这些游戏也将会相比以往的广告更自然地推送到我们面前。我们所看到短视频、直播、明星、广告都将成为游戏的宣传手段,而特定的目标又会被特定的游戏所针对。
当人们真正选择了一款游戏后,从某种角度来说,游戏要做的事就只有一个:让你爱上它。游戏成瘾是自游戏流行起来一直存在的话题。游戏给人带来的心流体验、一个充满奖杯的成就系统、令人心情激动的及时反馈等等,都在满足了玩家的各种需求的同时也让玩家沉迷于其中。在过去,游戏已经展现了其令人着迷的魔力,而在未来,这种力量将更加强大。目前已有游戏利用AI强化游戏里的内容。包括为玩家匹配合适的对手以及生成合适的敌人。游戏设计者也在获得大量的用户习惯数据后,做出相应的调整,使用户更容易沉迷其中。
玩家在失去自由意志时很容易被游戏的内容所影响,而这样的影响有时会在玩家离开游戏后依然生效。有时这样的影响不造成严重的后果,游戏公司可能也无意去这样做。但随着游戏产业的逐渐庞大,更多的人群把电子游戏作为自己的娱乐方式甚至是生活方式时,游戏同时也成为了一个宣传战场。令人担忧的是,这样的宣传可能是推销一件商品,可能是鼓励一种行为,也可能是推行一种价值观。玩家沉溺于其中却无法意识到其中的宣传,甚至当玩家从游戏中获得越多的成就感,越对游戏中的某种观念深信不疑。这种宣传会在游戏公司为游戏筛选了合适的玩家后更为有效。
正如我们提到的游戏的特征,玩家渴望成为其虚拟生活的因果代理。但是我们不得不承认,我们或许在没有意识到的情况下丧失了这种自由意志。具体来说,游戏通过设计,预制程序和算法例如目标,空间,和非人实体参与到我们思想和行为的产生。游戏者大脑的认知思维能力被游戏逐步训练成为习惯性行为。这种习惯就像一个过滤器,阻止更多意识的产生。这种潜移默化地被动接受的影响有风险将玩家转化成一种游戏种的机械化程序,执行输入和输出指令,当接收到某个信号。在现实世界中,自主权的丧失反映的是我们如何与我们周围环境的交互。许多艺术家和建筑学家都在研究这一领域。但在游戏这个主题下,自主权丧失所带来的影响有机会被延伸到现实生活中,并在未来造成社会的不安。
我们发现一个很有趣的问题,过去和现在的很多游戏无法归纳进维基百科游戏的定义(娱乐性,目的性,竞争性),比如过家家、任天堂switch推出的健身换大冒险、动物森友会等等。于是我们重新给出了游戏的定义,即在不严肃环境下完全自主的行为模拟。
我们通过研究几千年前到现在的游戏发展历史发现,人类和游戏关系中的角色一直在发生改变。
在远古时期,偶然诞生的游戏大部分是模拟生存技能训练。懂得通过游戏提高族群战斗力的人类部族基因在优胜劣汰中保存下来。游戏筛选人类。
在文艺复兴时期,人们彻底改变了对游戏的消极态度(中世纪时期,在教廷的影响下,玩和宗教无关的游戏被认为是不洁的行为)。人们在发现自我的同时,解放了对游戏的渴望。随着人性解放的过程,人们各种各样的需求被开发。但受限于当时生产力的低下,人类非常渴望游戏。
如今在各种技术的支持下(如游戏代码开源平台),我们有数不过来的游戏可以选择。人们在挑选时,会更有目的性。比如我喜欢第三人称射击类游戏,我不会在谷歌搜索游戏、射击游戏等模糊概念,而是直接搜索第三人称射击游戏。有的人渴望通过游戏与朋友们社交,有的人希望通过游戏提升自己的某项技能(比如微软公司的飞行模拟游戏)。人类选择游戏的阶段开始了。
我们通过对现象学和行为心理学的研究发现,游戏开始出现shape人类的情况。这种塑造不仅局限于游戏内,在现实生活中也会真实的影响人类个体乃至整个人类社会。我们发现游戏在潜移默化中,通过引诱、使沉迷和使服从这三个手段,改变了我们的行为模式甚至是价值观。
首先,拥有大数据的娱乐公司将会为我们安排他们认为的最适合我们的游戏。那些依靠大数据的算法将比我们自己更清楚我们会需要什么样的游戏。就像人们会花大量的时间在tictok。那些tictok中看似随机刷出的视频其实都是由软件公司的算法提供给我们的。于此同时,由于现在许多游戏公司很多属于一些娱乐企业的一部分。在这样的情况下,这些游戏也将会相比以往的广告更自然地推送到我们面前。我们所看到短视频、直播、明星、广告都将成为游戏的宣传手段,而特定的目标又会被特定的游戏所针对。
当人们真正选择了一款游戏后,从某种角度来说,游戏要做的事就只有一个:让你爱上它。游戏成瘾是自游戏流行起来一直存在的话题。游戏给人带来的心流体验、一个充满奖杯的成就系统、令人心情激动的及时反馈等等,都在满足了玩家的各种需求的同时也让玩家沉迷于其中。在过去,游戏已经展现了其令人着迷的魔力,而在未来,这种力量将更加强大。目前已有游戏利用AI强化游戏里的内容。包括为玩家匹配合适的对手以及生成合适的敌人。游戏设计者也在获得大量的用户习惯数据后,做出相应的调整,使用户更容易沉迷其中。
玩家在失去自由意志时很容易被游戏的内容所影响,而这样的影响有时会在玩家离开游戏后依然生效。有时这样的影响不造成严重的后果,游戏公司可能也无意去这样做。但随着游戏产业的逐渐庞大,更多的人群把电子游戏作为自己的娱乐方式甚至是生活方式时,游戏同时也成为了一个宣传战场。令人担忧的是,这样的宣传可能是推销一件商品,可能是鼓励一种行为,也可能是推行一种价值观。玩家沉溺于其中却无法意识到其中的宣传,甚至当玩家从游戏中获得越多的成就感,越对游戏中的某种观念深信不疑。这种宣传会在游戏公司为游戏筛选了合适的玩家后更为有效。
正如我们提到的游戏的特征,玩家渴望成为其虚拟生活的因果代理。但是我们不得不承认,我们或许在没有意识到的情况下丧失了这种自由意志。具体来说,游戏通过设计,预制程序和算法例如目标,空间,和非人实体参与到我们思想和行为的产生。游戏者大脑的认知思维能力被游戏逐步训练成为习惯性行为。这种习惯就像一个过滤器,阻止更多意识的产生。这种潜移默化地被动接受的影响有风险将玩家转化成一种游戏种的机械化程序,执行输入和输出指令,当接收到某个信号。在现实世界中,自主权的丧失反映的是我们如何与我们周围环境的交互。许多艺术家和建筑学家都在研究这一领域。但在游戏这个主题下,自主权丧失所带来的影响有机会被延伸到现实生活中,并在未来造成社会的不安。
In the context of product gamification, both positive and negative impacts on us from games will be magnified a lot in the future. Game, a friend who was born at the beginning of humankind, now needs to be reconsidered, from today’s perspective.
We found an exciting fact. Many past and current games cannot be summarized into the definition of games (entertainment, purpose, and competitiveness)given by Wikipedia, such as Doll House Play, Nintendo Switch’s fitness Adventure, and Animal Crossing. So we redefined game as completely autonomous behaviour simulation in a non-serious environment.
By studying the history of game development from thousands of years ago to the present, we have discovered that the role of human beings in the relationship with games has been changing all the way.
In ancient times, born by accident, most games were simulated survival skills training. The genes of human tribes who know how to improve the hunting ability through games are preserved in the race of survival. The game screens humans.
During the Renaissance, people completely changed their negative attitudes towards games (in the Middle Ages, under the influence of the Holy See, playing games unrelated to religion was considered as an unclean behaviour). While people were exploring themselves, they liberated their desire for games. With the liberation of human nature, people’s various needs are developed. But limited by the low productivity at that time, humans are very eager for access to games.
Today, with the support of various technologies (such as game open-code source platforms), we have countless games to choose from. People are more purposeful when making a choice. For example, I like third-person shooter games. Instead of searching for vague concepts such as games and shooting games on Google, I will directly search for third-person shooter games. Some people are eager to socialize with friends through games, and some others want to improve their skills through games (such as Microsoft’s flight simulation game). The stage of human choosing game begins.
Through our research on phenomenology and behavioural psychology, we have found that games have started to shape human. This kind of shaping is not only confined to the game itself but also affects individual humans and even the entire human society in real life. We found that the game is imperceptibly changing our behaviour patterns and even our values through the three stages of inducing, addicting and obeying.
The first is inducing. Entertainment companies with big data will show the games they think are best for us. Those algorithms that rely on big data will know better than ourselves when it comes to questions like what kind of games we will need, just like people spend a lot of time in Tic Tok. The seemingly random videos in Tic Tok are provided to us by algorithms. At the same time, many game companies are now part of some big entertainment groups.Under such circumstances, the stakeholders advertise specific games to us more reasonably. The short videos, live broadcasts, and advertisements will all become the propaganda for games. Algorithms not only know what we like but also when and how to let us meet the game.
After people choose a game, from a particular perspective, the only target the game has to do is to make you fall in love with it. Game addiction is always a hot topic since games became popular. The flow.experience (https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01682/full)that the game brings to us, an achievement system full of trophies, exciting feedback and so on, all satisfy the various needs of the players while also letting the players addict to it. In the past, games have shown their fascinating attraction, and in the future, this power will be even stronger. There are already some games that use AI to enhance the content in the game. Such as matching suitable opponents for the players and generating appropriate enemies. Game designers are also making corresponding adjustments after obtaining a large amount of user habits data to make it easier for users to indulge.
However, As we mention the new definition of games, players aspire to become the causal agents in the virtual world. They sincerely believe they do have such autonomy. But we have to admit that we may have lost this free will without realizing it. To be more specific, games are involved in the generation of our thoughts and actions through design and pre-made programs and algorithm, such as Targets, Spaces, and non-human entities. The cognitive thinking ability of players brain is gradually trained into habitual behaviour. This habit is like a filter, preventing more consciousness. The invisibly passive acceptance of the effect risks transforming players into a kind of mechanized program within a game, executing input and output instructions as receiving a signal as a trigger that developers have setup.
We found an exciting fact. Many past and current games cannot be summarized into the definition of games (entertainment, purpose, and competitiveness)given by Wikipedia, such as Doll House Play, Nintendo Switch’s fitness Adventure, and Animal Crossing. So we redefined game as completely autonomous behaviour simulation in a non-serious environment.
By studying the history of game development from thousands of years ago to the present, we have discovered that the role of human beings in the relationship with games has been changing all the way.
In ancient times, born by accident, most games were simulated survival skills training. The genes of human tribes who know how to improve the hunting ability through games are preserved in the race of survival. The game screens humans.
During the Renaissance, people completely changed their negative attitudes towards games (in the Middle Ages, under the influence of the Holy See, playing games unrelated to religion was considered as an unclean behaviour). While people were exploring themselves, they liberated their desire for games. With the liberation of human nature, people’s various needs are developed. But limited by the low productivity at that time, humans are very eager for access to games.
Today, with the support of various technologies (such as game open-code source platforms), we have countless games to choose from. People are more purposeful when making a choice. For example, I like third-person shooter games. Instead of searching for vague concepts such as games and shooting games on Google, I will directly search for third-person shooter games. Some people are eager to socialize with friends through games, and some others want to improve their skills through games (such as Microsoft’s flight simulation game). The stage of human choosing game begins.
Through our research on phenomenology and behavioural psychology, we have found that games have started to shape human. This kind of shaping is not only confined to the game itself but also affects individual humans and even the entire human society in real life. We found that the game is imperceptibly changing our behaviour patterns and even our values through the three stages of inducing, addicting and obeying.
The first is inducing. Entertainment companies with big data will show the games they think are best for us. Those algorithms that rely on big data will know better than ourselves when it comes to questions like what kind of games we will need, just like people spend a lot of time in Tic Tok. The seemingly random videos in Tic Tok are provided to us by algorithms. At the same time, many game companies are now part of some big entertainment groups.Under such circumstances, the stakeholders advertise specific games to us more reasonably. The short videos, live broadcasts, and advertisements will all become the propaganda for games. Algorithms not only know what we like but also when and how to let us meet the game.
After people choose a game, from a particular perspective, the only target the game has to do is to make you fall in love with it. Game addiction is always a hot topic since games became popular. The flow.experience (https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01682/full)that the game brings to us, an achievement system full of trophies, exciting feedback and so on, all satisfy the various needs of the players while also letting the players addict to it. In the past, games have shown their fascinating attraction, and in the future, this power will be even stronger. There are already some games that use AI to enhance the content in the game. Such as matching suitable opponents for the players and generating appropriate enemies. Game designers are also making corresponding adjustments after obtaining a large amount of user habits data to make it easier for users to indulge.
However, As we mention the new definition of games, players aspire to become the causal agents in the virtual world. They sincerely believe they do have such autonomy. But we have to admit that we may have lost this free will without realizing it. To be more specific, games are involved in the generation of our thoughts and actions through design and pre-made programs and algorithm, such as Targets, Spaces, and non-human entities. The cognitive thinking ability of players brain is gradually trained into habitual behaviour. This habit is like a filter, preventing more consciousness. The invisibly passive acceptance of the effect risks transforming players into a kind of mechanized program within a game, executing input and output instructions as receiving a signal as a trigger that developers have setup.





我们制作了一部微电影。用人与人的关系去映射人与游戏的关系,放大了游戏对人引诱、使沉迷、使服从的影响。我们希望观众能仔细观察游戏内的奖励机制和价值观冲击。
Games are challenging to define, especially in the context of today’s product gamification. More and more products in life can be defined as games. On the one hand, the impact of games on us will expand; on the other hand, the impact of games on people will become more and more complex and noway to describe. So we made a video, hoping to use the moments of daily life to metaphor the relationship between games and people. We believe that many people can find their reflections in this video.
Our team has been trying to maintain a neutral perspective on the topic of game autonomy. We believe that this unsettling fact exists for very reasonable and objective reasons. As one of the essential means of business, inducing is not a negative word itself. Immersion sounds more like a compliment to excellent service and experience. Then, everyone in this world has ever experienced like, doing things they don’t want to do. As an autonomous simulation that takes place in a non-serious situation, the game should not allow players to obey other people’s thoughts and values that much, because games exsist for that! However, the fact is that game developers are all from the real world. When a traditional game is born, it is like a controversial painting, which needs to be judged by the market and the audiences. That is how games work today, successfully but unsettling. We hope this project can convey our concerns about the loss of autonomy in the game, and at the same time allow people to experience this familiar, constant, virtual impact. Welcome to the gamified world.